Key points
- CDC recommends all pregnant patients be screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection during each pregnancy.
- Testing, screening, and timely treatment are essential for preventing perinatal transmission of HBV infection.
- CDC has tools and resources to help clinicians prevent perinatal hepatitis B transmission.
Why it's important
When a pregnant patient has HBV infection, it can pose a serious risk to their infant. Infants with perinatal HBV infection have a 90% chance of developing chronic HBV infection. 1
Testing pregnant patients for hepatitis B and providing pregnant patients and infants with appropriate treatment and vaccination is the best way to prevent perinatal HBV infection.
Preventing perinatal HBV transmission is an integral part of the national strategy to eliminate hepatitis B in the United States.
How to make decisions on whether to screen or test
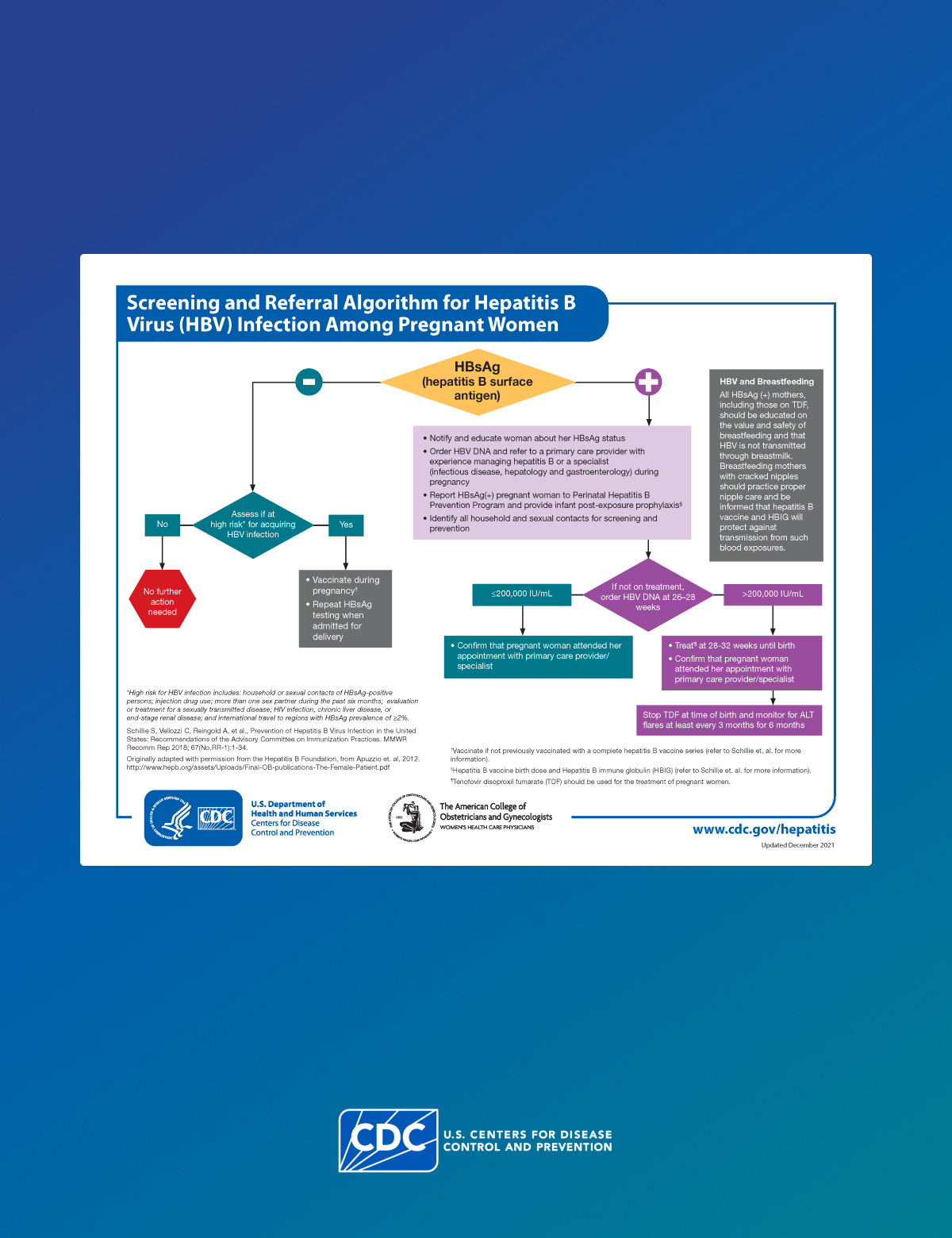
HBV infection can be identified in pregnant patients and infants by a confirmed positive hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) test result.
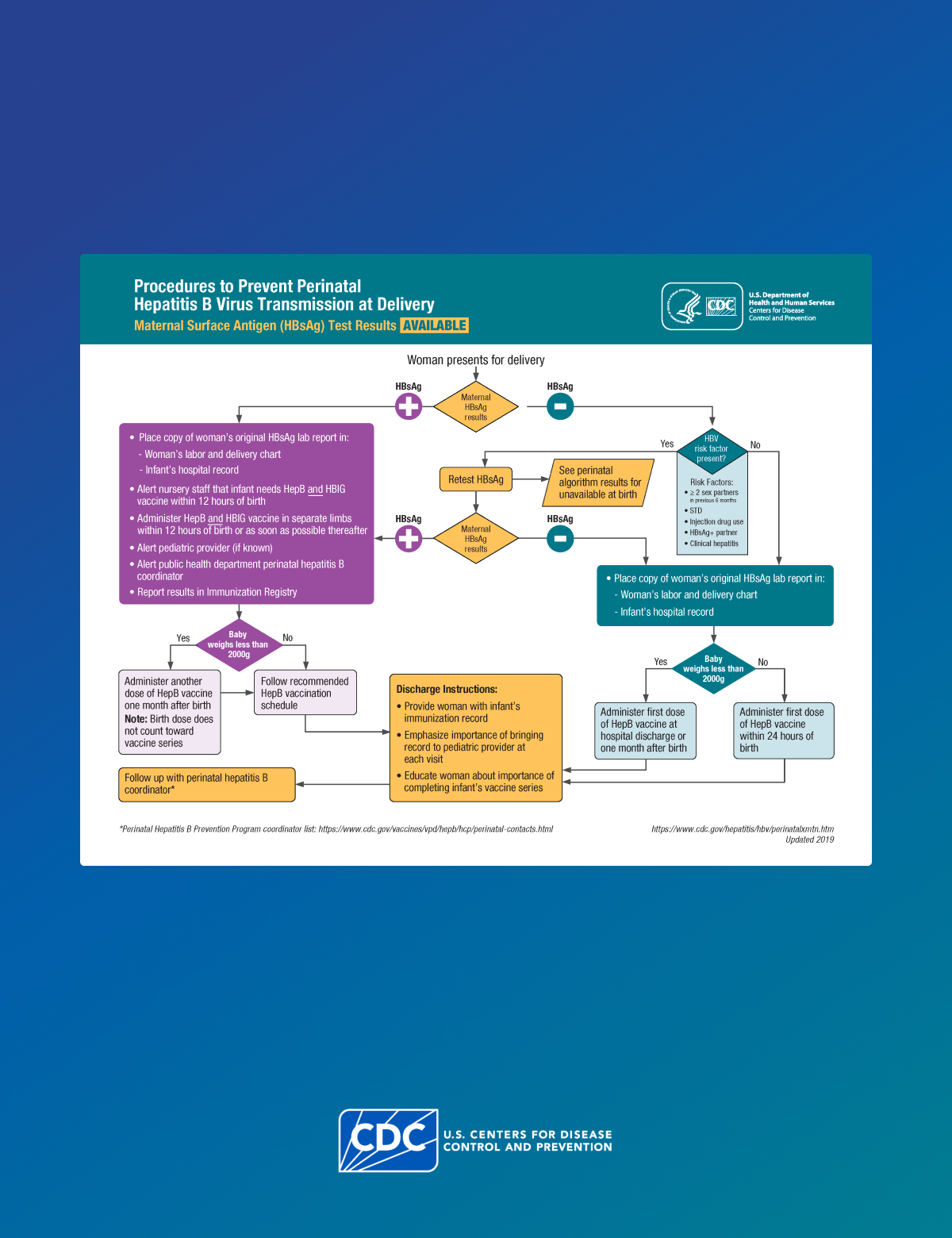
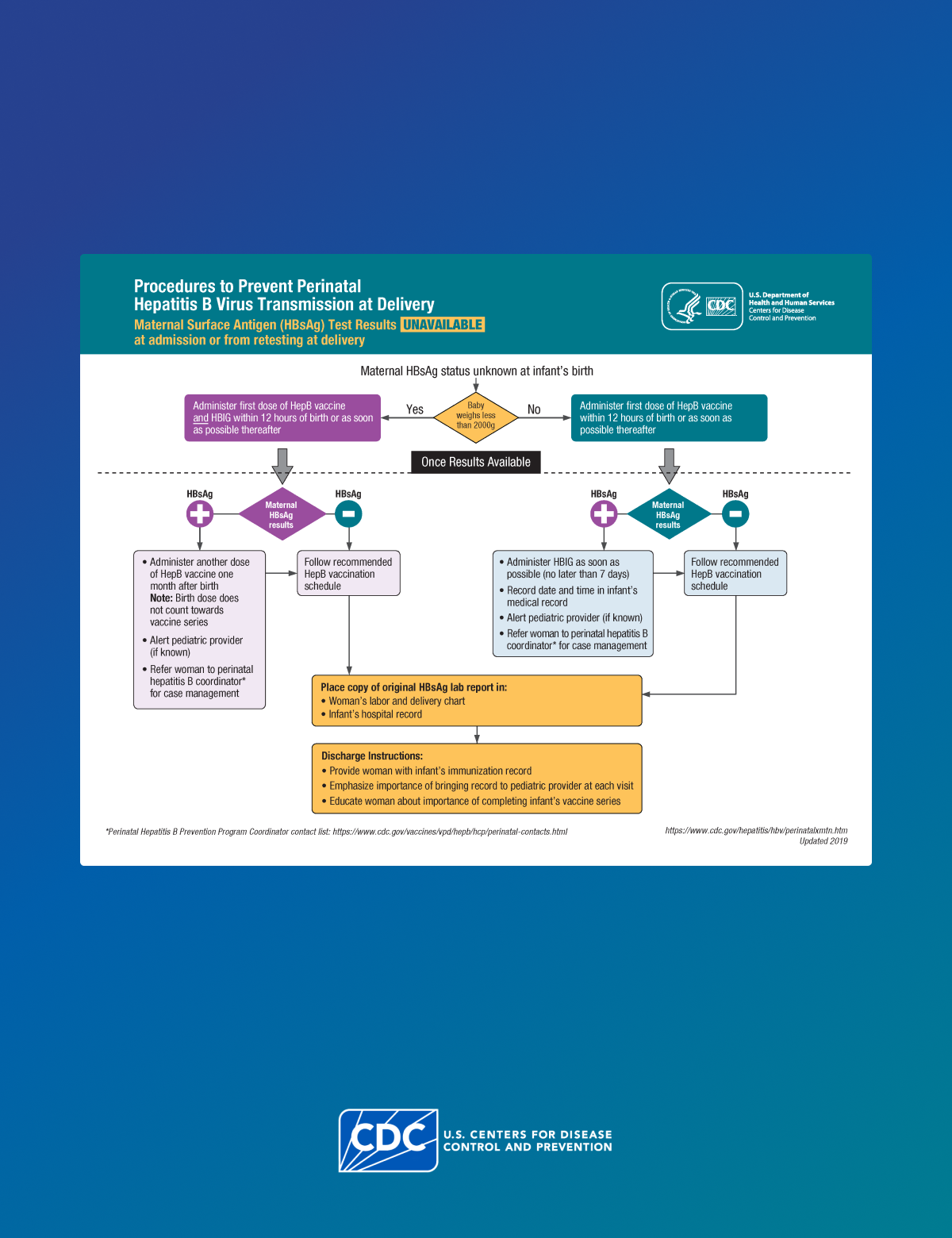
All pregnant patients who are HBsAg-positive should be referred to their jurisdiction's Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program (PHBPP)2 for case management to ensure that their infants receive timely postexposure immunoprophylaxis and follow-up.
Clinicians should provide a copy of the original laboratory report indicating the pregnant patient's HBsAg-positive test result to the:
- Hospital or birthing facility where the delivery is planned.
- Health care provider (HCP) who will care for the newborn.
To learn more about post-vaccination serologic testing (PVST) for infants, see Perinatal Postvaccination Testing guidelines.
Screening and testing guidelines
Clinicians should screen all pregnant patients for HBsAg during each pregnancy, preferably in the first trimester, regardless of:
- Vaccination status
- Chronic infection
- Testing history
Recommended tests
Pregnant patients
A confirmed positive HBsAg test result indicates current HBV infection.
Clinicians should test all pregnant patients who are HBsAg-positive for HBV DNA. This information will help the clinician make the decision to prescribe maternal antiviral therapy to prevent perinatal HBV transmission.
Infants and children
CDC recommends PVST for infants born to a person with a confirmed positive HBsAg test result. Serologic testing confirms whether the child has developed immunity or has HBV infection.
Clinicians should test all infants born to pregnant patients who are HBsAg-positive or have other evidence of HBV infection for HBsAg and antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) at 9–12 months of age, or 1–2 months after vaccine series completion if the series is delayed.
For information on how to interpret PVST results, refer to CDC's Management of Infants Born to Women with HBV Infection for Pediatricians.
What to do next
If a pregnant patients tests HBsAg-negative, clinicians should assess them to see if they're at a high risk for acquiring HBV infection.
If a pregnant patients tests HBsAg-positive, there are important steps to take to help inform care and prevent perinatal transmission to the infant.
Tip sheets
For more information on management of pregnant patients and infants born to patients with HBV infection, see the following resource:
Reporting cases
CDC recommends reporting all HBsAg-positive test results of pregnant patients to the state PHBPP. 2 Coordinators can follow up and ensure infants are evaluated appropriately.
Laboratory reporting
In 2013 and 2014, approximately 88% of commercially insured women and 84% of Medicaid-enrolled women were tested for HBsAg during pregnancy.3 Yet, fewer than half of the expected births to HBsAg-positive patients were identified.
CDC encourages all laboratories providing HBsAg testing services to capture pregnancy status to identify pregnant patients with HBV infection.
Clinicians and health departments can play a critical role in laboratory reporting of pregnancy status. HBsAg screening tests should be designated as "prenatal" or on a prenatal/obstetric panel when being ordered for a pregnant patients. Additionally, health departments should be aware of how laboratories reporting to their jurisdiction are reporting pregnancy information (e.g., including the word "prenatal," providing International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision [ICD-10] codes, etc.).
Resources
For clinicians seeking more information, CDC has several resources available concerning perinatal HBV.
CDC resources
Downloadable algorithms
American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) resources
Patient resources
Resources covering the preventative measures a parent with hepatitis B can take to protect their baby.
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (English)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (French)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Russian)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Burmese)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Chinese)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Hmong)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Khmer)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Korean)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Laotian)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Tagalog)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Vietnamese)
- When a Pregnant Woman Has Hepatitis B (Spanish)
Resources covers the benefits of hepatitis B vaccine for parents and their infants.
- Schillie S, Vellozzi C, Reingold A, et al. Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Recomm Rep 2018;67(No. RR-1):1–31.
- Koneru A, Fenlon N, Schillie S, et al. National Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program: 2009–2017. Pediatrics March 2021;147(3) e20201823.
- Kolasa MS, Tsai Y, Xu J, Fenlon N, Schillie S. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Testing Among Pregnant Women, United States 2014. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2017;36:e175–80.