At a glance
Overview
Successful execution of many PHDS milestones requires coordination, collaboration and partnership across CDC, federal agencies, healthcare partners and state, tribal, local and territorial (STLT) public health departments. Here are some examples of how CDC supports and engages with partners to realize the impact of the PHDS.
Funding for STLTs to modernize systems and data infrastructure. Since FY20, CDC has provided more than $1 billion directly to state, tribal, local and territorial public health departments and to nongovernmental partners to support data modernization efforts. Data modernization funding is provided to STLTs through the Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity program and the Public Health Infrastructure Grant. In addition, CDC provides technical assistance directly and through partner organizations to accelerate implementation of data modernization activities.
Hands-on support to implement new initiatives and technologies. In 2024, CDC provided $255 million to create four Implementation Centers. This program provides tailored support to public health agencies for data modernization and interoperability initiatives focused on data exchange between health care and public health, and among public health agencies.
Workforce development. CDC provides training opportunities directly and through funded public health partners to build data and technology-related skills across public health, including the Data Science Team Training program. Additionally, in 2024, CDC supported the Workforce Acceleration Initiative, that will place 140 skilled data and technology experts across 49 STLTs.
Regular forums for public health partner engagement. Convenings like the Consortium for Data Modernization and Industry Days help harmonize data modernization strategies and implementation across public health and health care. Thanks to public health partner engagement, the annual PHDS milestone revision process for 2025 was informed by feedback from over 500 participants.
Playbook and implementation guidance. A variety of engagements and publications highlight successful data modernization efforts across the public health ecosystem, such as Data Modernization in Action.
Human-centered design and impact-oriented product development approaches. CDC is bringing together expertise in human-centered design and technology to help inform the development of products to meet the needs of public health. In 2024, CDC created a comprehensive service design blueprint outlining needs, pain points and opportunities in case data exchange. This effort included a human-centered design approach and a cross-disciplinary summit with dozens of participants across the public health ecosystem.
Learn more about how CDC works with partners to advance data modernization efforts.
What is the public health ecosystem?
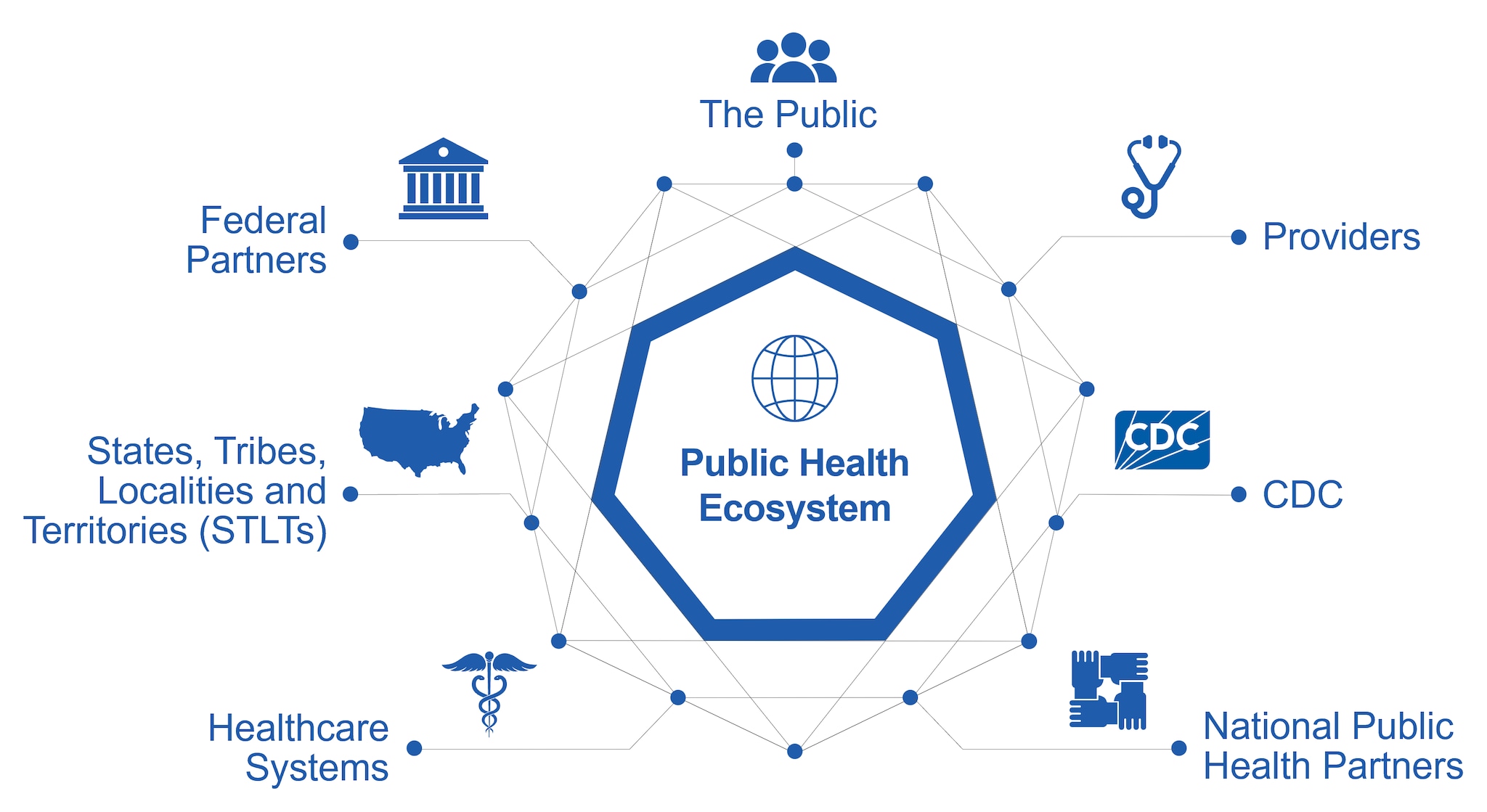
"Public health ecosystem" describes public health's connectivity across the nation for systems that depend on, influence, and interact with each other. This ecosystem also includes the workforce, policies, and technologies used to collect, manage, access, share, analyze, and disseminate the most relevant data.
The PHDS sets a roadmap for the ecosystem to improve our communities and keep people safe. There are many actors in the ecosystem that have critical roles in data and action for public health. It takes a coordinated effort to make progress in data exchange.